Page 14 - ATHM26_4
P. 14
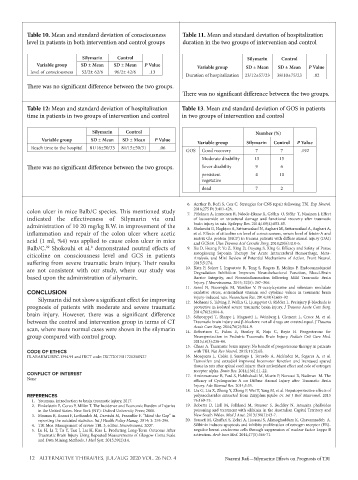
Table 10. Mean and standard deviation of consciousness Table 11. Mean and standard deviation of hospitalization
level in patients in both intervention and control groups duration in the two groups of intervention and control
Silymarin Control Silymarin Control
Variable group SD ± Mean SD ± Mean P Value Variable group SD ± Mean SD ± Mean P Value
level of consciousness 52/2± 62/6 96/2± 42/6 .13
Duration of hospitalization 23/12±57/23 38/10±75/23 .82
There was no significant difference between the two groups.
There was no significant difference between the two groups.
Table 12: Mean and standard deviation of hospitalization Table 13. Mean and standard deviation of GOS in patients
time in patients in two groups of intervention and control in two groups of intervention and control
Silymarin Control Number (%)
Variable group SD ± Mean SD ± Mean P Value Variable group Silymarin Control P Value
Reach time to the hospital 81/16±50/33 81/15±50/31 .06 GOS Good recovery 7 7 .192
Moderate disability 13 15
There was no significant difference between the two groups. Sever disability 9 6
persistent 4 10
vegetative
dead 7 2
6. Aertker B, Bedi S, Cox C. Strategies for CNS repair following TBI. Exp Neurol.
2016;275 Pt 3:411-426.
colon ulcer in mice Balb/C species. This mentioned study 7. Pitkänen A, Immonen R, Ndode-Ekane X, Gröhn O, Stöhr T, Nissinen J. Effect
indicated the effectiveness of Silymarin via oral of lacosamide on structural damage and functional recovery after traumatic
brain injury in rats. Epilepsy Res. 2014;108(4):653-65.
administration of 10 20 mg/kg B.W. in improvement of the 8. Shokouhi G, Haghjoo A, Sattarnezhad N, Asghari M, Sattarnezhad A, Asghari A,
inflammation and repair of the colon ulcer where acetic et al. Effects of citicoline on level of consciousness, serum level of fetuin-A and
acid (1 ml, %4) was applied to cause colon ulcer in mice matrix Gla-protein (MGP) in trauma patients with diffuse axonal injury (DAI)
and GCS≤8. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2014;20(6):410-6.
Balb/C. Shokouhi et al. demonstrated neutral effects of 9. Xu D, Huang P, Yu Z, Xing D, Ouyang S, Xing G. Efficacy and Safety of Panax
29
8
citicoline on consciousness level and GCS in patients notoginseng Saponin Therapy for Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage, Meta-
Analysis, and Mini Review of Potential Mechanisms of Action. Front Neurol.
suffering from severe traumatic brain injury. Their results 2015;5:274.
are not consistent with our study, where our study was 10. Katz P, Sulzer J, Impastato R, Teng S, Rogers E, Molina P. Endocannabinoid
Degradation Inhibition Improves Neurobehavioral Function, Blood-Brain
based upon the administration of silymarin. Barrier Integrity, and Neuroinflammation following Mild Traumatic Brain
Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2015; 32(5): 297–306.
11. Senol N, Nazıroğlu M, Yürüker V. N-acetylcysteine and selenium modulate
CONCLUSION oxidative stress, antioxidant vitamin and cytokine values in traumatic brain
injury-induced rats. Neurochem Res. 2014;39(4):685-92
Silymarin did not show a significant effect for improving 12. Mohseni S, Talving P, Wallin G, Ljungqvist O, Riddez L. Preinjury β-blockade is
prognosis of patients with moderate and severe traumatic protective in isolated severe traumatic brain injury. J Trauma Acute Care Surg.
2014;76(3):804-8.
brain injury. However, there was a significant difference 13. Schroeppel T, Sharpe J, Magnotti L, Weinberg J, Clement L, Croce M, et al.
between the control and intervention group in terms of CT Traumatic brain injury and β-blockers: not all drugs are created equal. J Trauma
Acute Care Surg. 2014;76(2):504-9.
scan, where more normal cases were shown in the silymarin 14. Robertson C, Fidan E, Stanley R, Noje C, Bayir H. Progesterone for
group compared with control group. Neuroprotection in Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury. Pediatr Crit Care Med.
2015;16(3):236-44.
15. Chase A. Traumatic brain injury: No benefit of progesterone therapy in patients
CODE OF ETHICS with TBI. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015;11(2):65.
IR.ARAKMU.REC.1394.91 and IRCT code: IRCT2017011720258N27 16. Mosquera L, Colón J, Santiago J, Torrado A, Meléndez M, Segarra A, et al.
Tamoxifen and estradiol improved locomotor function and increased spared
tissue in rats after spinal cord injury: their antioxidant effect and role of estrogen
receptor alpha. Brain Res. 2014;1561:11-22.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST 17. Aminmansour B, Fard S, Habibabadi M, Moein P, Norouzi R, Naderan M. The
None efficacy of Cyclosporine-A on Diffuse Axonal Injury after Traumatic Brain
Injury. Adv Biomed Res. 2014;3:35.
18. Liu G, Liu X, Zhang Y, Zhang F, Wei T, Yang M, et al. Hepatoprotective effects of
REFERENCES polysaccharides extracted from Zizyphus jujube cv. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015
1. Youmans. introduction to brain traumatic injury, 2017. 76:169-75.
2. Finkelstein E, Corso P, Miller T. The Incidence and Economic Burden of Injuries 19. Roberts D, Hall M, Falkland M, Strasser S, Buckley N. Amanita phalloides
in the United States. New York (NY): Oxford University Press; 2006. poisoning and treatment with silibinin in the Australian Capital Territory and
3. Moazen B, Rezaei F, Lotfizadeh M, Darvishi M, Farzadfar F. “Mind the Gap” in New South Wales. Med J Aust. 2013;198(1):43-7.
reporting the outdated statistics. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2014; 3: 295-296. 20. Yousefi M, Ghaffari S, Zekri A, Hassani S, Alimoghaddam K, Ghavamzadeh A.
4. TBI Mos. Management of severe TBI. 3, editor. Neurotrauma. 2007. Silibinin induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation of estrogen receptor (ER)-
5. Lu H, Li T, Tu Y, Tsai J, Lai H, Kuo L. Predicting Long-Term Outcome After negative breast carcinoma cells through suppression of nuclear factor kappa B
Traumatic Brain Injury Using Repeated Measurements of Glasgow Coma Scale activation. Arch Iran Med. 2014;17(5):366-71.
and Data Mining Methods. J Med Syst. 2015;39(2):14.
12 ALTERNATIVE THERAPIES, JUL/AUG 2020 VOL. 26 NO. 4 Nazemi Rafi—Silymarine Effects on Prognosis of TBI