Page 43 - ATHM26_4
P. 43
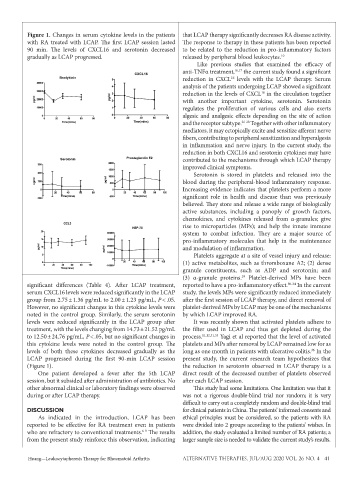
Figure 1. Changes in serum cytokine levels in the patients that LCAP therapy significantly decreases RA disease activity.
with RA treated with LCAP. The first LCAP session lasted The response to therapy in these patients has been reported
90 min. The levels of CXCL16 and serotonin decreased to be related to the reduction in pro-inflammatory factors
gradually as LCAP progressed. released by peripheral blood leukocytes. 10
Like previous studies that examined the efficacy of
anti-TNFα treatment, 16,17 the current study found a significant
reduction in CXCL levels with the LCAP therapy. Serum
16
analysis of the patients undergoing LCAP showed a significant
reduction in the levels of CXCL in the circulation together
16
with another important cytokine, serotonin. Serotonin
regulates the proliferation of various cells and also exerts
algesic and analgesic effects depending on the site of action
and the receptor subtype. 26-28 Together with other inflammatory
mediators, it may ectopically excite and sensitize afferent nerve
fibers, contributing to peripheral sensitization and hyperalgesia
in inflammation and nerve injury. In the current study, the
reduction in both CXCL16 and serotonin cytokines may have
contributed to the mechanisms through which LCAP therapy
improved clinical symptoms.
Serotonin is stored in platelets and released into the
blood during the peripheral-blood inflammatory response.
Increasing evidence indicates that platelets perform a more
significant role in health and disease than was previously
believed. They store and release a wide range of biologically
active substances, including a panoply of growth factors,
chemokines, and cytokines released from α-granules; give
rise to microparticles (MPs); and help the innate immune
system to combat infection. They are a major source of
pro-inflammatory molecules that help in the maintenance
and modulation of inflammation.
Platelets aggregate at a site of vessel injury and release:
(1) active metabolites, such as thromboxane A2; (2) dense
granule constituents, such as ADP and serotonin; and
(3) α-granule proteins. Platelet-derived MPs have been
29
significant differences (Table 4). After LCAP treatment, reported to have a pro-inflammatory effect. 30-34 In the current
serum CXCL16 levels were reduced significantly in the LCAP study, the levels MPs were significantly reduced immediately
group from 2.75 ± 1.36 pg/mL to 2.00 ± 1.23 pg/mL, P < .05. after the first session of LCAP therapy, and direct removal of
However, no significant changes in this cytokine levels were platelet-derived MPs by LCAP may be one of the mechanisms
noted in the control group. Similarly, the serum serotonin by which LCAP improved RA.
levels were reduced significantly in the LCAP group after It was recently shown that activated platelets adhere to
treatment, with the levels changing from 14.73 ± 21.52 pg/mL the filter used in LCAP and thus get depleted during the
to 12.50 ± 24.76 pg/mL, P < .05, but no significant changes in process. 11,12,31,35 Yagi et al reported that the level of activated
this cytokine levels were noted in the control group. The platelets and MPs after removal by LCAP remained low for as
levels of both these cytokines decreased gradually as the long as one month in patients with ulcerative colitis. In the
36
LCAP progressed during the first 90-min LCAP session present study, the current research team hypothesizes that
(Figure 1). the reduction in serotonin observed in LCAP therapy is a
One patient developed a fever after the 5th LCAP direct result of the decreased number of platelets observed
session, but it subsided after administration of antibiotics. No after each LCAP session.
other abnormal clinical or laboratory findings were observed This study had some limitations. One limitation was that it
during or after LCAP therapy. was not a rigorous double-blind trial nor random; it is very
difficult to carry out a completely random and double-blind trial
DISCUSSION for clinical patients in China. The patients’ informed consents and
As indicated in the introduction, LCAP has been ethical principles must be considered, so the patients with RA
reported to be effective for RA treatment even in patients were divided into 2 groups according to the patients’ wishes. In
who are refractory to conventional treatments. The results addition, the study evaluated a limited number of RA patients; a
6-9
from the present study reinforce this observation, indicating larger sample size is needed to validate the current study’s results.
Huang—Leukocytapheresis Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis ALTERNATIVE THERAPIES, JUL/AUG 2020 VOL. 26 NO. 4 41