Page 46 - ATHM26_4
P. 46
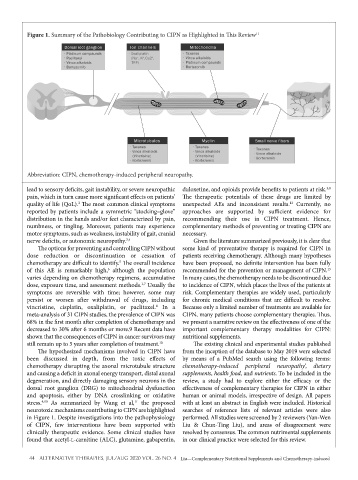
Figure 1. Summary of the Pathobiology Contributing to CIPN as Highlighted in This Review 11
Abbreviation: CIPN, chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy.
lead to sensory deficits, gait instability, or severe neuropathic duloxetine, and opioids provide benefits to patients at risk.
3,8
pain, which in turn cause more significant effects on patients’ The therapeutic potentials of these drugs are limited by
quality of life (QoL). The most common clinical symptoms unexpected AEs and inconsistent results. Currently, no
3
12
reported by patients include a symmetric “stocking–glove” approaches are supported by sufficient evidence for
distribution in the hands and/or feet characterized by pain, recommending their use in CIPN treatment. Hence,
numbness, or tingling. Moreover, patients may experience complementary methods of preventing or treating CIPN are
motor symptoms, such as weakness, instability of gait, cranial necessary.
nerve deficits, or autonomic neuropathy. 3,4 Given the literature summarized previously, it is clear that
The options for preventing and controlling CIPN without some kind of preventative therapy is required for CIPN in
dose reduction or discontinuation or cessation of patients receiving chemotherapy. Although many hypotheses
chemotherapy are difficult to identify. The overall incidence have been proposed, no definite intervention has been fully
5
of this AE is remarkably high, although the population recommended for the prevention or management of CIPN.
6
13
varies depending on chemotherapy regimens, accumulative In many cases, the chemotherapy needs to be discontinued due
dose, exposure time, and assessment methods. Usually the to incidence of CIPN, which places the lives of the patients at
1,7
symptoms are reversible with time; however, some may risk. Complementary therapies are widely used, particularly
persist or worsen after withdrawal of drugs, including for chronic medical conditions that are difficult to resolve.
vincristine, cisplatin, oxaliplatin, or paclitaxel. In a Because only a limited number of treatments are available for
8
meta-analysis of 31 CIPN studies, the prevalence of CIPN was CIPN, many patients choose complementary therapies. Thus,
68% in the first month after completion of chemotherapy and we present a narrative review on the effectiveness of one of the
decreased to 30% after 6 months or more.9 Recent data have important complementary therapy modalities for CIPN:
shown that the consequences of CIPN in cancer survivors may nutritional supplements.
still remain up to 5 years after completion of treatment. The existing clinical and experimental studies published
10
The hypothesized mechanisms involved in CIPN have from the inception of the database to May 2019 were selected
been discussed in depth, from the toxic effects of by means of a PubMed search using the following terms:
chemotherapy disrupting the axonal microtubule structure chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy’, dietary
and causing a deficit in axonal energy transport, distal axonal supplements, health food, and nutrients. To be included in the
degeneration, and directly damaging sensory neurons in the review, a study had to explore either the efficacy or the
dorsal root ganglion (DRG) to mitochondrial dysfunction effectiveness of complementary therapies for CIPN in either
and apoptosis, either by DNA crosslinking or oxidative human or animal models, irrespective of design. All papers
stress. As summarized by Wang et al, the proposed with at least an abstract in English were included. Historical
11
4,10
neurotoxic mechanisms contributing to CIPN are highlighted searches of reference lists of relevant articles were also
in Figure 1. Despite investigations into the pathophysiology performed. All studies were screened by 2 reviewers (Yan-Wen
of CIPN, few interventions have been supported with Liu & Chun-Ting Liu), and areas of disagreement were
clinically therapeutic evidence. Some clinical studies have resolved by consensus. The common nutrimental supplements
found that acetyl-L-carnitine (ALC), glutamine, gabapentin, in our clinical practice were selected for this review.
44 ALTERNATIVE THERAPIES, JUL/AUG 2020 VOL. 26 NO. 4 Liu—Complementary Nutritional Supplements and Chemotherapy-induced