Page 56 - ATHM26_4
P. 56
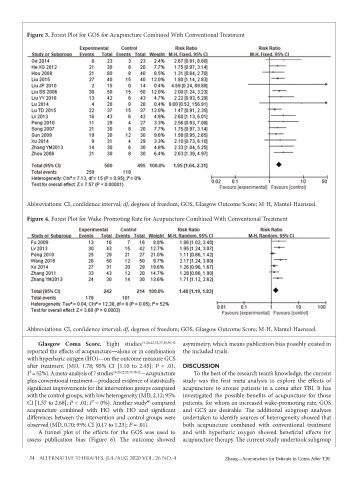
Figure 3. Forest Plot for GOS for Acupuncture Combined With Conventional Treatment
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; df, degrees of freedom; GOS, Glasgow Outcome Score; M-H, Mantel-Haenszel.
Figure 4. Forest Plot for Wake-Promoting Rate for Acupuncture Combined With Conventional Treatment
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; df, degrees of freedom; GOS, Glasgow Outcome Score; M-H, Mantel-Haenszel.
Glasgow Coma Score. Eight studies 19,20,22,32,37,38,40,42 asymmetry, which means publication bias possibly existed in
reported the effects of acupuncture—alone or in combination the included trials.
with hyperbaric oxygen (HO)—on the outcome measure GCS
after treatment (MD, 1.78; 95% CI [1.10 to 2.45]; P < .01; DISCUSSION
I² = 52%). A meta-analysis of 7 studies 19,20,22,32,37,38,42 —acupuncture To the best of the research team’s knowledge, the current
plus conventional treatment—produced evidence of statistically study was the first meta analysis to explore the effects of
significant improvements for the intervention groups compared acupuncture to arouse patients in a coma after TBI. It has
with the control groups, with low heterogeneity (MD, 2.12; 95% investigated the possible benefits of acupuncture for those
CI [1.57 to 2.68]; P < .01; I² = 0%). Another study compared patients, for whom an increased wake-promoting rate, GOS
40
acupuncture combined with HO with HO and significant and GCS are desirable. The additional subgroup analyses
differences between the intervention and control groups were undertaken to identify sources of heterogeneity showed that
observed (MD, 0.70; 95% CI [0.17 to 1.23]; P = .01). both acupuncture combined with conventional treatment
A funnel plot of the effects for the GOS was used to and with hyperbaric oxygen showed beneficial effects for
assess publication bias (Figure 6). The outcome showed acupuncture therapy. The current study undertook subgroup
54 ALTERNATIVE THERAPIES, JUL/AUG 2020 VOL. 26 NO. 4 Zhang—Acupuncture for Patients in Coma After TBI