Page 62 - ATHM26_4
P. 62
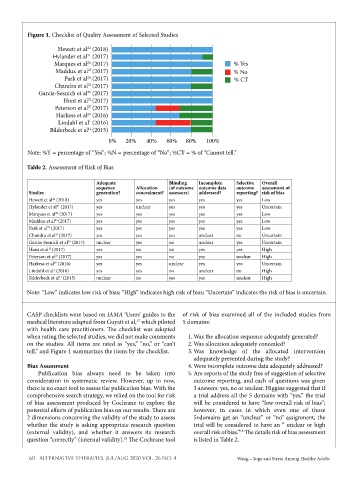
Figure 1. Checklist of Quality Assessment of Selected Studies
Hewett et al (2018)
22
Hylander et al (2017)
31
Marques et al (2017) % Yes
26
Maddux et al (2017) % No
25
Park et al (2017) % CT
24
Chandra et al (2017)
23
Garcia-Sesnich et al (2017)
28
Hunt et al (2017)
32
Peterson et al (2017)
27
Harkess et al (2016)
29
Lindahl et al (2016)
1
Bilderbeck et al (2015)
11
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
Note: %Y = percentage of “Yes”; %N = percentage of “No”; %CT = % of “Cannot tell.”
Table 2. Assessment of Risk of Bias
Adequate Blinding Incomplete Selective Overall
sequence Allocation (of outcome outcome data outcome assessment of
Studies generation? concealment? assessors) addressed? reporting? risk of bias
Hewett et al (2018) yes yes yes yes yes Low
22
Hylander et al (2017) yes unclear yes yes yes Uncertain
31
Marques et al (2017) yes yes yes yes yes Low
26
Maddux et al (2017) yes yes yes yes yes Low
25
Park et al (2017) yes yes yes yes yes Low
24
Chandra et al (2017) yes yes yes unclear no Uncertain
23
Garcia-Sesnich et al (2017) unclear yes no unclear yes Uncertain
28
Hunt et al (2017) yes no no yes yes High
32
Peterson et al (2017) yes yes no yes unclear High
27
Harkess et al (2016) yes yes unclear yes yes Uncertain
29
Lindahl et al (2016) yes yes no unclear no High
1
11
Bilderbeck et al (2015) unclear no yes yes unclear High
Note: “Low” indicates low risk of bias; “High” indicates high risk of bias; “Uncertain” indicates the risk of bias is uncertain.
CASP checklists were based on JAMA ‘Users’ guides to the of risk of bias examined all of the included studies from
medical literature adapted from Guyatt et al, which piloted 5 domains:
17
with health care practitioners. The checklist was adopted
when rating the selected studies, we did not make comments 1. Was the allocation sequence adequately generated?
on the studies. All items are rated as “yes,” “no,” or “can’t 2. Was allocation adequately concealed?
tell,” and Figure 1 summarizes the items by the checklist. 3. Was knowledge of the allocated intervention
adequately prevented during the study?
Bias Assessment 4. Were incomplete outcome data adequately addressed?
Publication bias always need to be taken into 5. Are reports of the study free of suggestion of selective
consideration in systematic review. However, up to now, outcome reporting, and each of questions was given
there is no exact tool to assess the publication bias. With the 3 answers: yes, no or unclear. Higgins suggested that if
comprehensive search strategy, we relied on the tool for risk a trial address all the 5 domains with “yes,” the trial
of bias assessment produced by Cochrane to explore the will be considered to have “low overall risk of bias”;
potential effects of publication bias on our results. There are however, in cases in which even one of those
2 dimensions concerning the validity of the study to assess 5vdomains get an “unclear” or “no“ assignment, the
whether the study is asking appropriate research question trial will be considered to have an “ unclear or high
(external validity), and whether it answers its research overall risk of bias.” The details risk of bias assessment
18
question “correctly” (internal validity). The Cochrane tool is listed in Table 2.
18
60 ALTERNATIVE THERAPIES, JUL/AUG 2020 VOL. 26 NO. 4 Wang—Yoga and Stress Among Healthy Adults